Individual Health Insurance Nevada
Health insurance is among the most important purchases you’ll ever make. Comparing health plans and obtaining personal health insurance quotes and information has never been easy. Thanks to the Affordable Care Act, also known as Obamacare, you have consumer protection on your side.
Before 2014, one could purchase an individual health insurance plan at any time of the year. But as of now, one can only buy individual health insurance during open enrollment, except for special circumstances.
Do I Need Individual Health Insurance?
The Obamacare mandate requires that most people obtain medical insurance coverage. If you are not already enrolled in a health plan that meets the Affordable Care Act minimum essential benefits requirements, you may need to switch plans.
The mandate requires that most Americans and legal residents obtain health insurance that meets the standards set by the Nevada Exchange. Those who do not get health insurance may face a penalty. For assistance with your application, please call 702-996-4627.
You may also need to get Individual Health Insurance in Nevada if:
- You are self-employed.
- Your employer does not offer group plans.
- You are enrolled in a group plan, but it does not cover
- your spouse or dependents.
- You are enrolled in a health plan, but the premiums are too high.
- You are enrolled in a health plan, but your benefit needs have changed.
Pros and Cons of Individual Health Insurance
For some, personal health insurance is the only way to meet ACA requirements, If you have the option of group health insurance, personal health insurance plans may still be the better option. It all comes down to which plan best meets your needs.
Individual health insurance has several benefits, such as:
- More control: Individual plans allow you to choose from a wider plan selection than just the ones your employer presents to you. You can find a more customized solution that includes what you need and excludes what you don’t.
- Flexibility: Personal health insurance is not tied to your employment. This can be useful if you are concerned about job loss or changing positions. You can even use it to “close a gap” between an insufficient employer-provided plan and your healthcare needs.
- Choice of insurer: You can choose from more insurers with an individual plan. Some will have certain benefits, customer service offerings, or pricing models that are more appealing to you.
On the other hand, individual health insurance also has some downsides:
- Higher costs: Often, a group plan is partially paid for by the employer and has lower premiums in the first place. Without these savings, individual plans can be slightly more expensive.
- Pre-existing condition coverage: Individual plans may charge additional fees or lack coverage if you have a pre-existing condition.
Types of Individual Health Insurance
Individual health plans vary in how they are structured and how much they pay for your health costs. Under the ACA, all health plans must meet certain minimum essential coverage, meaning that no one can be denied during the Open Enrollment Period for any pre-existing medical conditions.
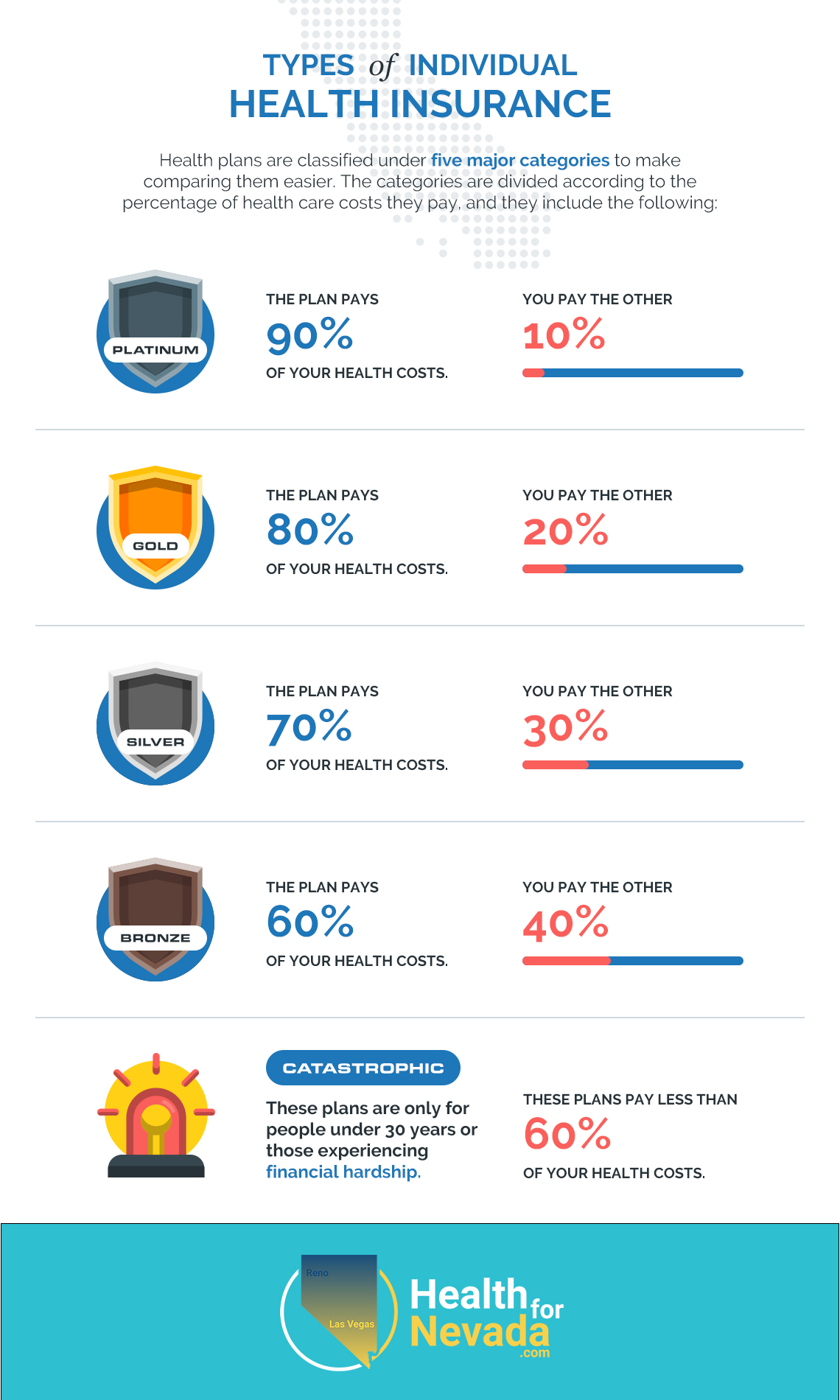
Health plans are classified under five major categories to make comparing them easier. The categories are divided according to the percentage of health care costs they pay, and they include the following:
- Platinum – Plan pays 90% of your health costs. You pay 10%.
- Gold – Plan pays 80% of your health costs. You pay 20%.
- Silver – Plan pays 70% of your health costs. You pay 30%.
- Bronze – Plan pays 60% of your health costs. You pay 40%.
- Catastrophic – These plans are only for people under 30 years old or those experiencing financial hardship. These plans pay less than 60% of your health care costs.
With these categories, you’ll also find different structures:
- Health maintenance organization (HMO): HMOs provide low out-of-pocket costs with a limited choice of providers and out-of-network coverage only in emergencies. These plans revolve around seeing a primary care doctor who can make specialist referrals.
- Preferred provider organization (PPO): A PPO has higher out-of-pocket costs than an HMO but with more flexibility. You don’t need a referral to see a specialist, and you have more provider options, including some coverage for out-of-network providers.
- Exclusive provider organization (EPO): EPOs have lower premiums than PPOs and don’t require referrals, but provider choices are more limited. Seeing an out-of-network provider in a non-emergency setting will not be included.
- Point-of-Service Plan (POS): This kind of plan generally offers more choices of providers than an HMO but still requires referrals for specialists. Like a PPO, in-network care is less expensive than out-of-network care.
Choosing the Plan That’s Right for You
Choosing a personal health insurance plan that best fits your needs depends on a few different factors. Consider the following aspects and determine how they’ll affect your plan:
- Provider eligibility and choice: Want to keep your current doctor? Please make sure they’re in-network first. Also, ensure you’re comfortable with the providers included in the plan.
- Medication eligibility: Medication coverage can vary widely by form, brand, and prior approval requirements. If you take regular medications, you’ll want to make sure they’re included appropriately.
- Premiums vs. out-of-pocket costs: If you frequently visit the doctor, lower copayments can be easier to manage but will have higher premiums. Alternatively, if you rarely see a doctor, lower premiums and higher out-of-pocket costs might be a good choice.
- Network resources: If you don’t have much patience for phone calls, reimbursements and paperwork, you may want to look for a provider with particularly strong customer service or few requirements on your end.
Buying Nevada Individual Health Insurance
Before purchasing personal health insurance, you need to think about your health care needs and budget. Then, compare various plans to find the most suitable fit. Here are some questions you need to consider.
- How is the plan structured?
- Which providers are in the network?
- What is included by the plan?
- How much out-of-pocket costs do you pay?
- How much does the plan pay for your coverage?

Think about your budget as well as your healthcare needs, and find out how much it will cost you in insurance premiums and out-of-pocket costs for every plan you consider. Nevada makes it easier to compare different plans and choose the one that fits your individual health needs and budget.
Making a smart choice in health insurance isn’t easy, but the research you do now will pay off later when you need health care for yourself and your family. Take advantage of our online services at Health for CA Insurance Center to get free, instant quotes on Nevada health insurance plans for individuals. Just fill out our confidential form to get started.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) Plans: A type of plan that has a network of preferred providers from which you can choose. Your plan may assign a primary care provider to assist in coordination of care. However, the member may still coordinate their own care and can see any provider within the network without a referral. Members can also see providers outside the network, but at a higher cost.


